Proposed threat model
Starting from the components illustrated in the Architecture page, OWASP Threat Dragon and the STRIDE model were used to identify threats. They are grouped below by the functionality that enables them.
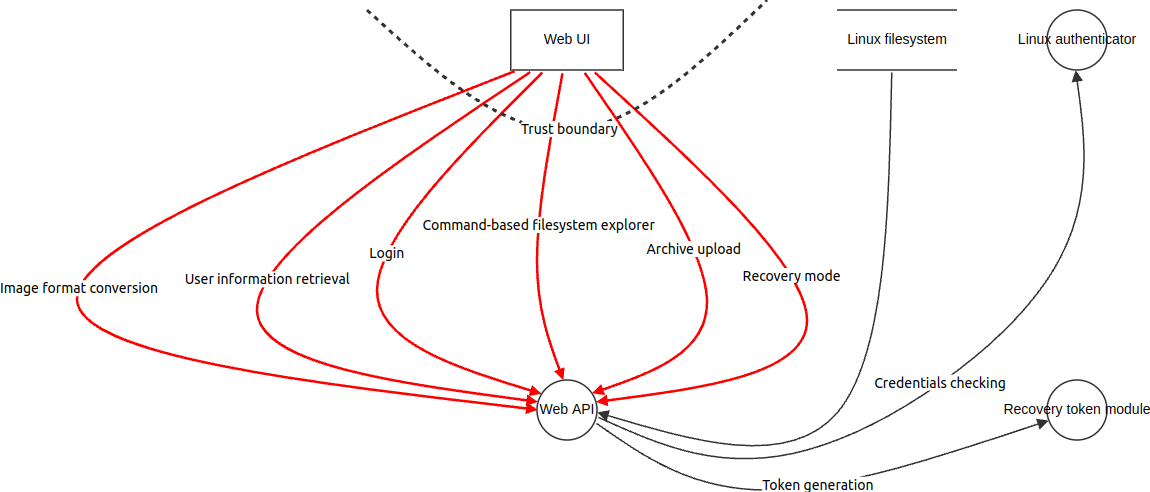
Identified threats
note
The list of threats is not exhaustive. Please see the contribution guide to propose new threats.
Image format conversion
- DoS with large images: An attacker can upload multiple large images, which are heavily processed by the server to obtain the converted image, leading to a denial of service.
- Unrestricted storage location: An attacker can upload its image to an arbitrary location.
- Unrestricted file type upload: An attacker can upload any file type, leading to undefined behaviour.
Login
- Brute-forcing: An attacker can brute-force the credentials of the server.
- User enumeration via error codes: An attacker can identify the valid usernames by serving the error codes returned by the website when failing to log in.
- Timing attacks: An attacker is able to observe timing differences when validating credentials.
User information retrieval
- Unauthorized access to other information: An attacker can access information about other users on the system.
Command-based file explorer
- Arbitrary command execution: An attacker can bypass the allow list and execute any command.
- Access to system files or files of other users: An attacker can use the commands to access files which are owned by the system or other users.
- DoS with resource intensive commands: An attacker can execute commands which consume huge amounts of resources, leading to a denial of service.
Archive upload
- Unrestricted storage location: An attacker can upload its archives to an arbitrary location.
- Unrestricted file type upload: An attacker can upload any file type, leading to undefined behaviour.
- DoS with large archives or bombs: An attacker can upload multiple large images or a bomb, which are heavily processed by the server or occupy a huge amount of space, leading to a denial of service.
Recovery mode
- Token forging: An attacker can forge a valid recovery token.
- Valid token exfiltration: An attacker can extract a valid token of another user.
- User enumeration via error codes: An attacker can identify the valid usernames by serving the error codes returned by the website when failing to log in.
Exported threat model
The OWASP Threat Dragon model is available under the repository, in the others/threat-model.json JSON file.